Zoned/Multizone/Multicell & Distributed Wattage Cartridge Heaters, Platen Cartridge Heaters, Electric Heated Platens, Gundrilled Platens
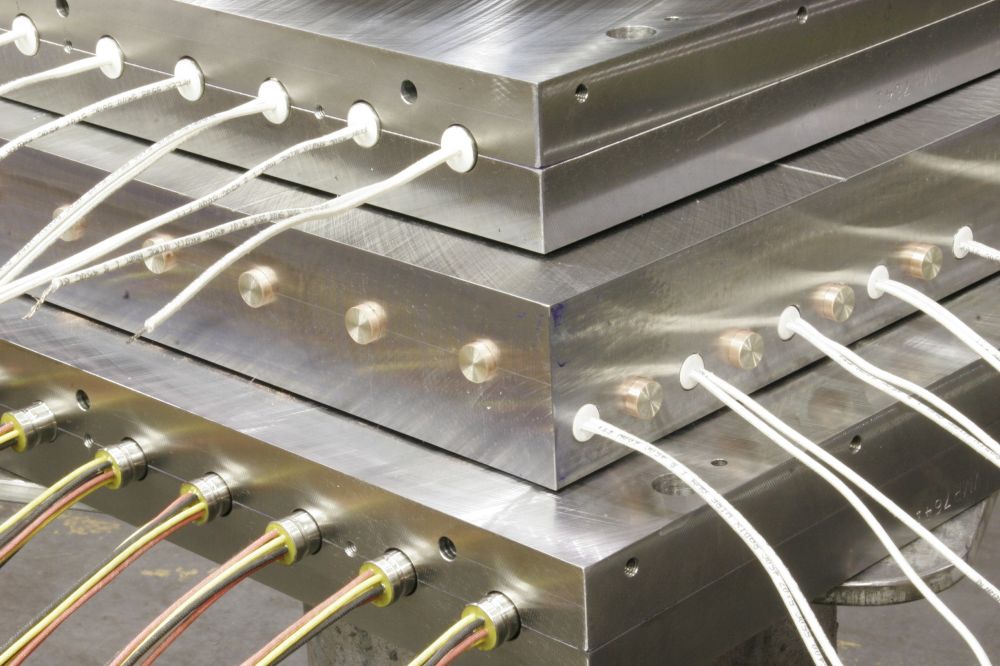

Mulizone/Multicell and Distributed Wattage Cartridge Heaters, Platen Heaters
Custom Multizone and Distributed Wattage Cartridge Heaters (Platen Heaters) - Zoned Versus
Distributed Wattage - Definition and Application:
In many industrial process heating applications we are often asked, what is the difference between
"distributed wattage" and "zoned/multizoned" (multicell) cartridge heaters? These
custom construction techniques are often applied to various heater types that transfer their heat via
conduction. Some examples are cartridge insertion heaters, ceramic and mica band heaters as well as mica
strip heaters. Usually most heaters that use a wound coil can use these construction methods to control
watt density. Let's discuss some definitions before beginning.
Definitions for the Construction of Zoned/ Multizoned and Distributed Wattage Cartridge Heaters:
Coil: A resistance wire usually Nickel/Chromium (often referred
to as Nichrome) that is wound around a round mandrel or ceramic core to hold the shape. When a coil
is wound, it is usually done in a uniform manner.
Close Wound: If all the turns of a wound coil touch, this is called a close wound coil.
Open Coil: If the close wound coil is taken and stretched, it becomes an open wound coil. Coils can also be initially wound as open coils if there is spacing between each turn of the coil.
Pitch: The distance from turn to turn of an open coil.
Watt Density: The wattage produced by a heater divided by the surface area of the heater. Common units of measure are W/in² and W/cm².
Close Wound: If all the turns of a wound coil touch, this is called a close wound coil.
Open Coil: If the close wound coil is taken and stretched, it becomes an open wound coil. Coils can also be initially wound as open coils if there is spacing between each turn of the coil.
Pitch: The distance from turn to turn of an open coil.
Watt Density: The wattage produced by a heater divided by the surface area of the heater. Common units of measure are W/in² and W/cm².
What Makes Distributed Wattage Cartridge Heaters:
Distributed wattage is when a coil winding's pitch is not consistent
throughout its entire length. Some parts of the winding are more tightly packed or wound with turns
than other sections, to allow the heat profile to be more concentrated in some areas of the heater
than another. The non-uniform pitched coil will have sections of closely wound coils and sections of
loosely wound coils. These methods of non-uniform stretching or non-uniform winding of the coil
pitch allow the heater manufacturer to increase or decrease the watt density of the heater in
certain sections. Because the coil winding in some of the sections will be closer together
than other sections, the watt density will be greater in those sections. These higher watt
density heater sections will be hotter than the other sections. Certain sections of the heater
can be now be made to run hotter than other sections. Only one set of power leads is used in
this configuration, as the entire heater turns on as one unit.
Application of Distributed Wattage Cartridge/Insertion Heaters
:
A distributed wattage heater allows the end user to have higher heat where needed. This method of distributing heat is especially beneficial if only a small section of the heater is providing the majority of the heating or in applications where heat is needed over a long length and there tends to be a greater temperature loss (heat loss) or drop-off near the heater ends. Distributed wattage heaters are often used in platens and sealing bar applications where heat loss compensation near the ends of the heater is critical.
A distributed wattage heater allows the end user to have higher heat where needed. This method of distributing heat is especially beneficial if only a small section of the heater is providing the majority of the heating or in applications where heat is needed over a long length and there tends to be a greater temperature loss (heat loss) or drop-off near the heater ends. Distributed wattage heaters are often used in platens and sealing bar applications where heat loss compensation near the ends of the heater is critical.
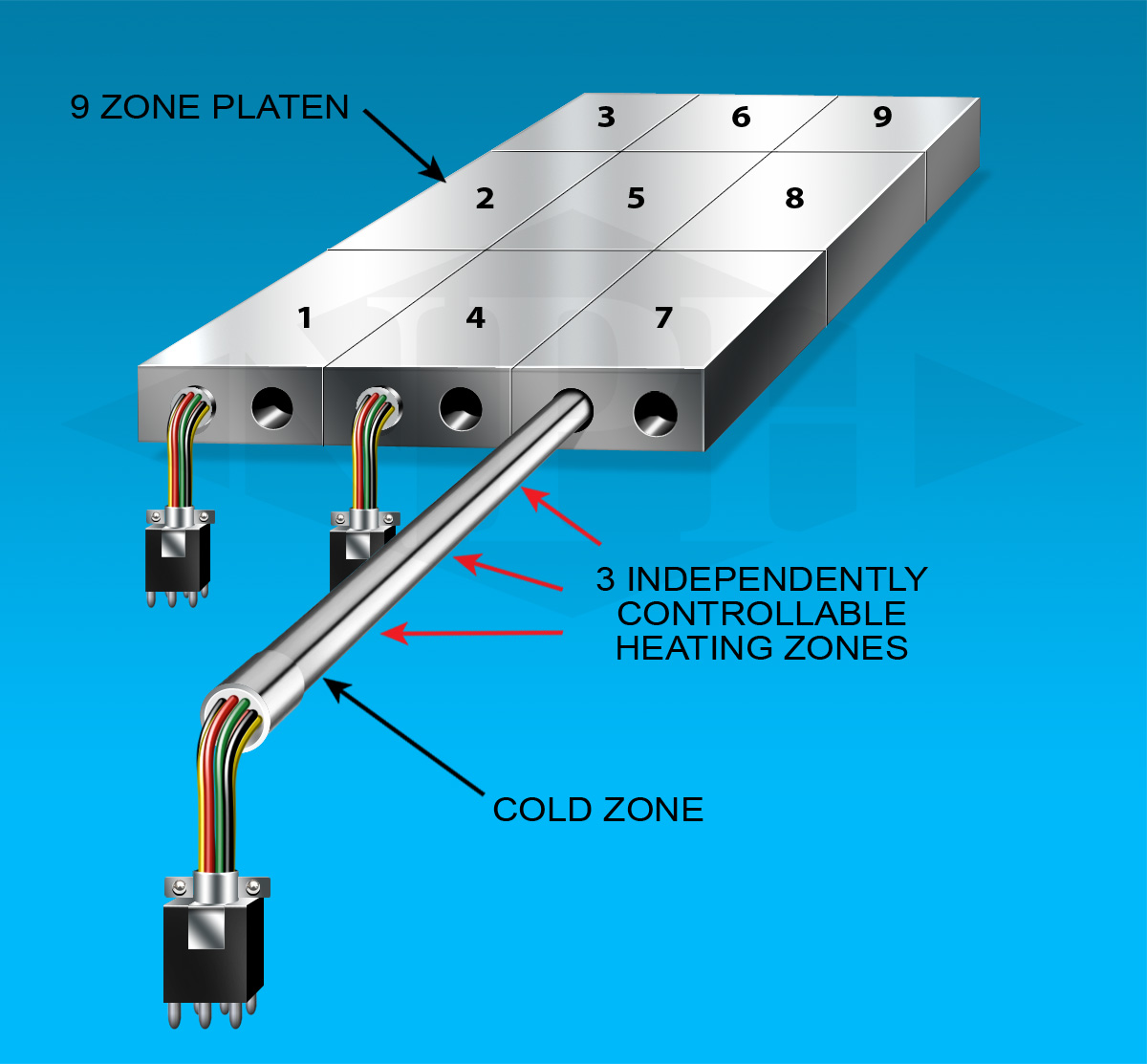
Distributed Wattage/Zoned/Multizone/Multicell Cartridge Heaters For Platens and Other Industrial
Applications
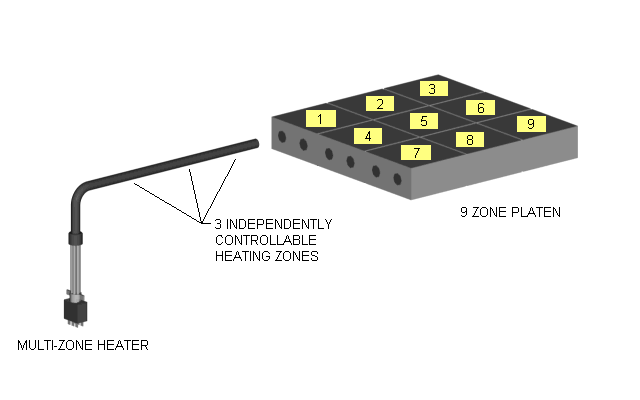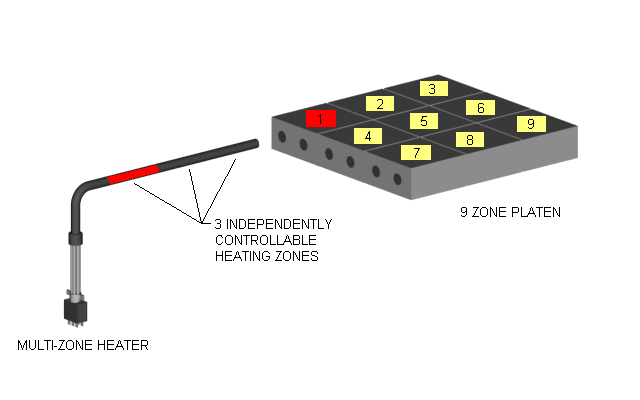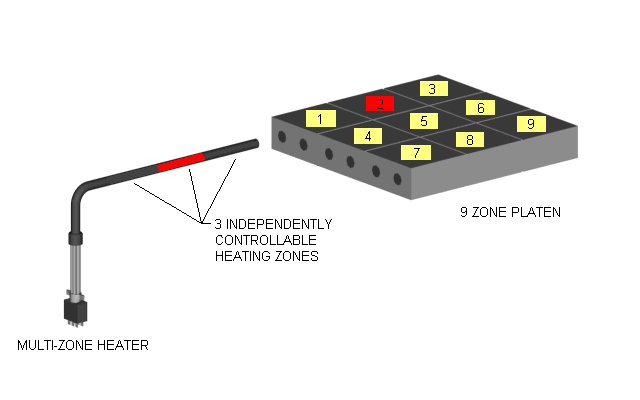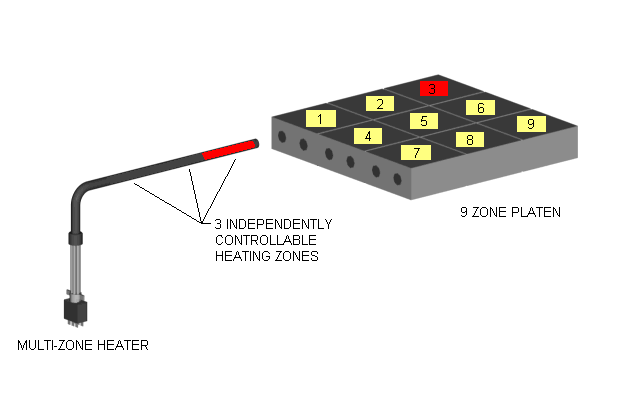
Multi Zone or Multi-Cell Cartridge Heaters with Three Independently Controllable Zones
or Distributed Wattage Options
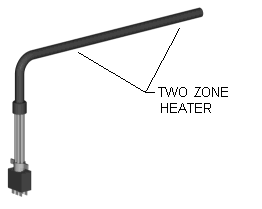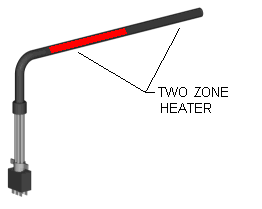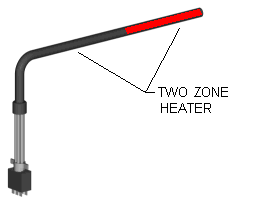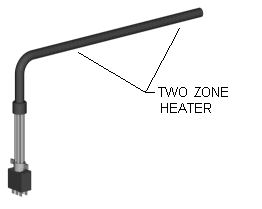
Images of Cartridge Heaters Above with One to Three Independently Controllable Zones or
Distributed Wattage Options
Zoned Heater or Multicell/Multizoned Cartridge Heaters:
Zoned heating is where a specific section of the heater has its own "dedicated" wound coil with uniform pitch and its own set of power leads for each particular section of a heater. The internal coil construction within this particular type of heater has sections or zones of dedicated uniformly wound coils. The key word in this construction style is "dedicated". The customer can literally control each section of heater individually. The heated area is very specific and controllable. For example a 2-zone heater will have 4 power leads coming out of it; a pair of leads for each zone. Sometimes a common wire may be used; in this 2-zone example, the number of leads can be reduced because each zoned coil shares a common lead. A heater like this would have 3 power leads.
Zoned heating is where a specific section of the heater has its own "dedicated" wound coil with uniform pitch and its own set of power leads for each particular section of a heater. The internal coil construction within this particular type of heater has sections or zones of dedicated uniformly wound coils. The key word in this construction style is "dedicated". The customer can literally control each section of heater individually. The heated area is very specific and controllable. For example a 2-zone heater will have 4 power leads coming out of it; a pair of leads for each zone. Sometimes a common wire may be used; in this 2-zone example, the number of leads can be reduced because each zoned coil shares a common lead. A heater like this would have 3 power leads.
Application of Zoned Wattage Cartridge Heaters:
Zoned heaters can be used in any application distributed wattage heaters are
used, but in most cases this would probably be over kill and not justify the added expense of the
zoned or multicell cartridge heater. Zoned heaters are best used in applications requiring a
significant level of heat control over of the length of the heater. Multizoned cartridge
heaters can have various sections literally turned off entirely while only a fraction of the entire
heater is energized. These insertion heaters are commonly used in heater bar(sealing bar)
applications where heat control at precise locations is an important factor.
Application of Cartridge Heaters in Gundrilled
Platens/Plates-Aluminun, Stainless Steel & Steel:
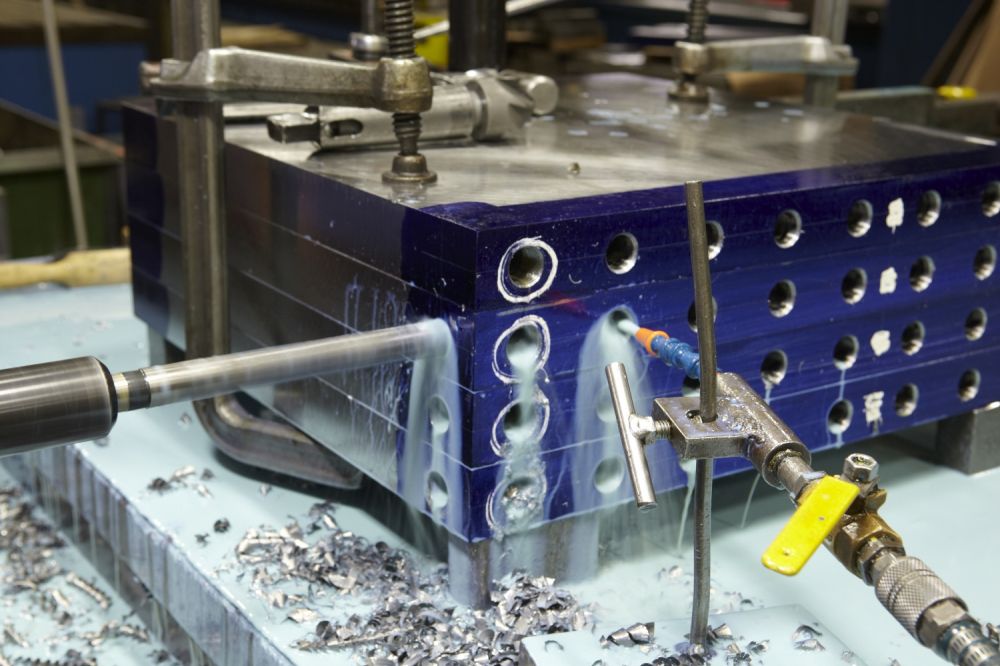

Gundrilled Platens/Plates and Mold Bases - Electric Heated Platens Using Cartridge
Heaters
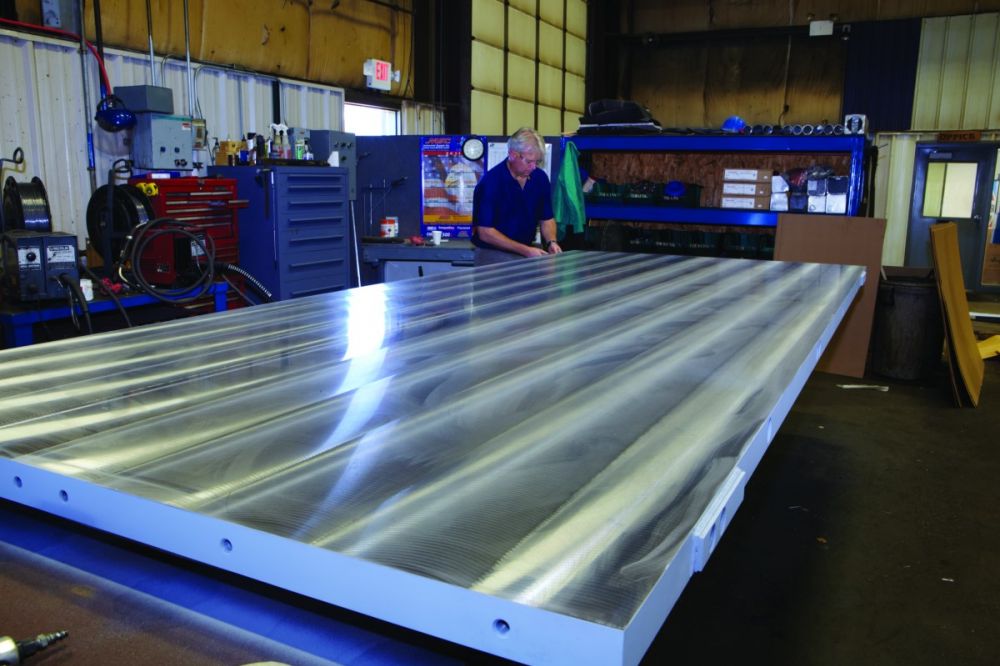

Long Hole Gundrilled Platens - Final Inspection
How To Order Cartridge Heaters




We Ship Our Kapton & Process Heaters To OEM’s & Industry World Wide
